SL Math - Analysis and Approaches - 1¶
The course code for this page is MHF4U7.
Review¶
Logarithm rules¶
The logarithm of a product can be rewritten as the sum of two logarithms.
The logarithm of a quotient can be rewritten as the difference of two logarithms.
The exponentials of a logarithm can be brought down to be coefficients.
Some simple values can be easily found.
3 - Geometry and trigonometry¶
To find the result of a primary trig ratio, the related acute angle (RAA) should first be found before referring to the CAST rule to determine quadrants before identifying all correct answers in the domain.
Circles¶
The equation below is true for every point on a circle with radius .
The area of a sector requires knowledge of the radius and angle in radians that the sector encompasses.
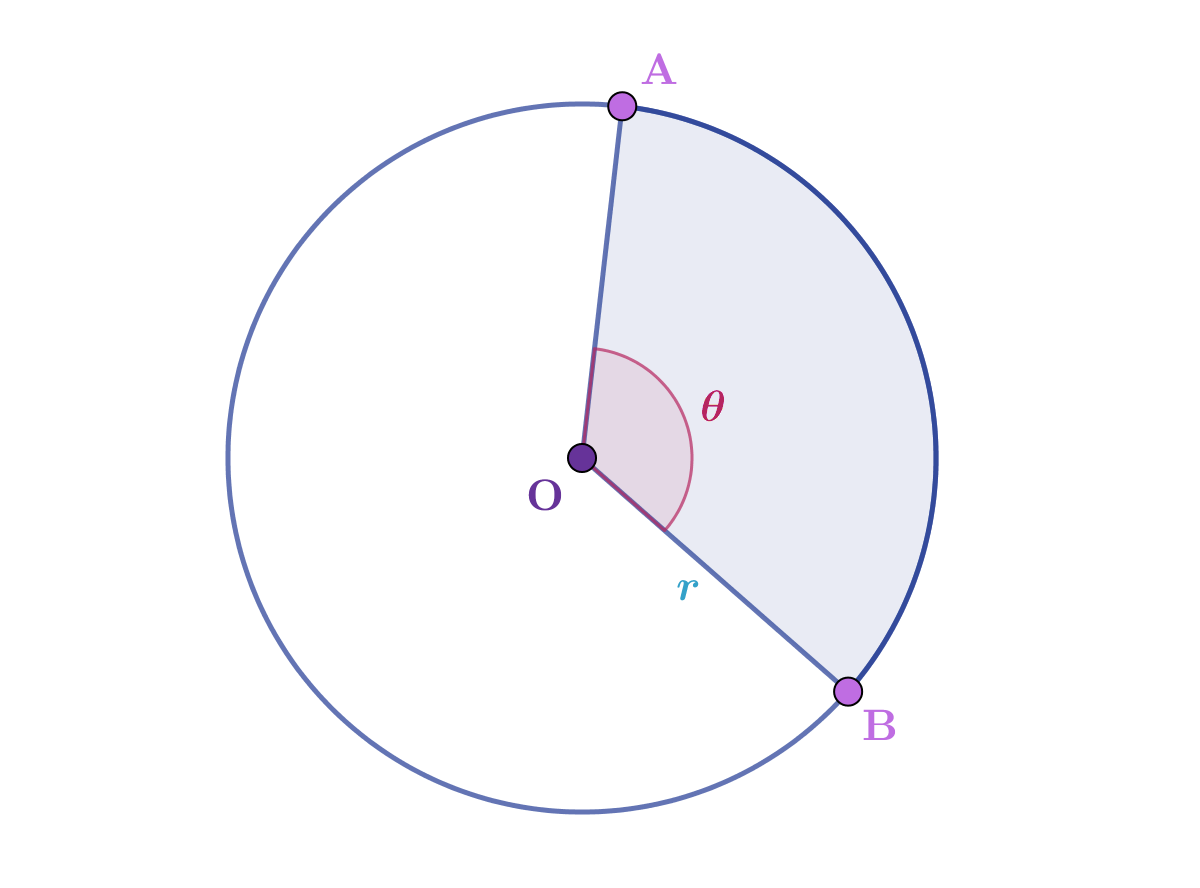 (Source: Kognity)
(Source: Kognity)
Trigonometric identities¶
The Pythagorean identity relates the radius of a circle to its x and y components.
The quotient identity relates the side lengths of a right-angled triangle.
The double angle identities can be used to convert one trig ratio to another.
Euler's number¶
Euler's number is a constant irrational number represented as a special limit in calculus.
The inverse of is , which is known as the natural logarithm and can be rewritten as ("lawn x").
4 - Statistics and probability¶
Definition
- Statistics: The techniques and procedures to analyse, interpret, display, and make decisions based on data.
- Descriptive statistics: The use of methods to work with and describe the entire data set.
- Inferential statistics: The use of samples to make judgements about a population.
- Data set: A collection of data with elements and observations, typically in the form of a table. It is similar to a map or dictionary in programming.
- Element: The name of an observation(s), similar to a key to a map/dictionary in programming.
- Observation: The collected data linked to an element, similar to a value to a map/dictionary in programming.
- Population: A collection of all elements of interest within a data set.
- Sample: The selection of a few elements within a population to represent that population.
- Raw data: Data collected prior to processing or ranking.
Sampling¶
A good sample:
- represents the relevant features of the full population,
- is as large as reasonably possible so that it decently represents the full population,
- and is random.
The types of random sampling include:
- Simple: Choosing a sample completely randomly.
- Convenience: Choosing a sample based on ease of access to the data.
- Systematic: Choosing a random starting point, then choosing the rest of the sample at a consistent interval in a list.
- Quota: Choosing a sample whose members have specific characteristics.
- Stratified: Choosing a sample so that the proportion of specific characteristics matches that of the population.
Example
- Simple: Using a random number generator to pick items from a list.
- Convenience: Asking the first 20 people met to answer a survey,
- Systematic: Rolling a die and getting a 6, so choosing the 6th element and every 10th element after that.
- Quota: Ensuring that all members of the sample all wear red jackets.
- Stratified: The population is 45% male and 55% female, so the proportion of the sample is also 45% male and 55% female.
Types of data¶
Definition
- Quantitative variable: A variable that is numerical and can be sorted.
- Discrete variable: A quantitative variable that is countable.
- Continuous variable: A quantitative variable that can contain an infinite number of values between any two values.
- Qualitative variable: A variable that is not numerical and cannot be sorted.
- Bias: An unfair influence in data during the collection process, causing the data to be not truly representative of the population.
Frequency distribution¶
A frequency distribution is a table that lists categories/ranges and the number of values in each category/range.
A frequency distribution table includes:
- A number of classes, all of the same width.
- This number is arbitrarily chosen, but a commonly used formula is .
- The width (size) of each class is .
- Each class includes its lower bound and excludes its upper bound ()
- The relative frequency of a data set is the percentage of the whole data set present in that class in decimal form.
- The number of values that fall under each class.
- The largest value can either be included in the final class (changing its range to ), or put in a completely new class above the largest class.
Example
| Height (cm) | Frequency |
|---|---|
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 1 |
For a given class , the midpoint of that class is as follows:
Quartiles¶
A percentile is a value indicates the percentage of a data set that is below it. To find the location of a given percentile, , where denotes the percentile number and represents the sample size.
A decile indicates that % of data in the data set is below it.
Example
A score equal to or greater than 97% of all scores in a test is said to be in the 97th percentile, or in the 9th decile.
Quartiles split a data set into four equal sections.
- The minimum is the lowest value of a data set.
- The first quartile () is at the 25th percentile.
- The median is at the 50th percentile.
- The third quartile () is at the 75th percentile.
- The maximum is the highest value of a data set.
The first and third quartiles are the median of the [minimum, median) and (median, maximum] respectively.
Warning
When the median is equal to a data point in a set, it cannot be used to find or . Only use the data below or above the median.
Warning
When working with grouped data given in ranges, the actual data is unavailable. The five numbers above are instead:
- The minimum value is now the lower class boundary of the lowest class.
- The first and third quartiles, as well as the median, are now found by guesstimating the value on a cumulative frequency curve.
- The maximum value is now the upper class boundary of the highest class. If the highest value is excluded (e.g., ), it also must be excluded when representing data (e.g., open dot instead of filled dot).
- A specific percentile can be found by guesstimating the value on a cumulative frequency curve.
The interquartile range (IQR) is equal to and represents the range where 50% of the data lies.
Outliers¶
Outliers are data values that significantly differ from the rest of the data set. They may be because of:
- a random natural occurrence, or
- abnormal circumstances
Outliers can be ignored once identified.
There are various methods to identify outliers. For single-variable data sets, the lower and upper fences may be used. Any data below the lower fence or above the upper fence can be considered outliers.
- The lower fence is equal to
- The upper fence is equal to
Representing frequency¶
A stem and leaf plot can list out all the data points while grouping them simultaneously.
A frequency histogram can be used to represent frequency distribution, with the x-axis containing class boundaries, and the y-axis representing frequency.
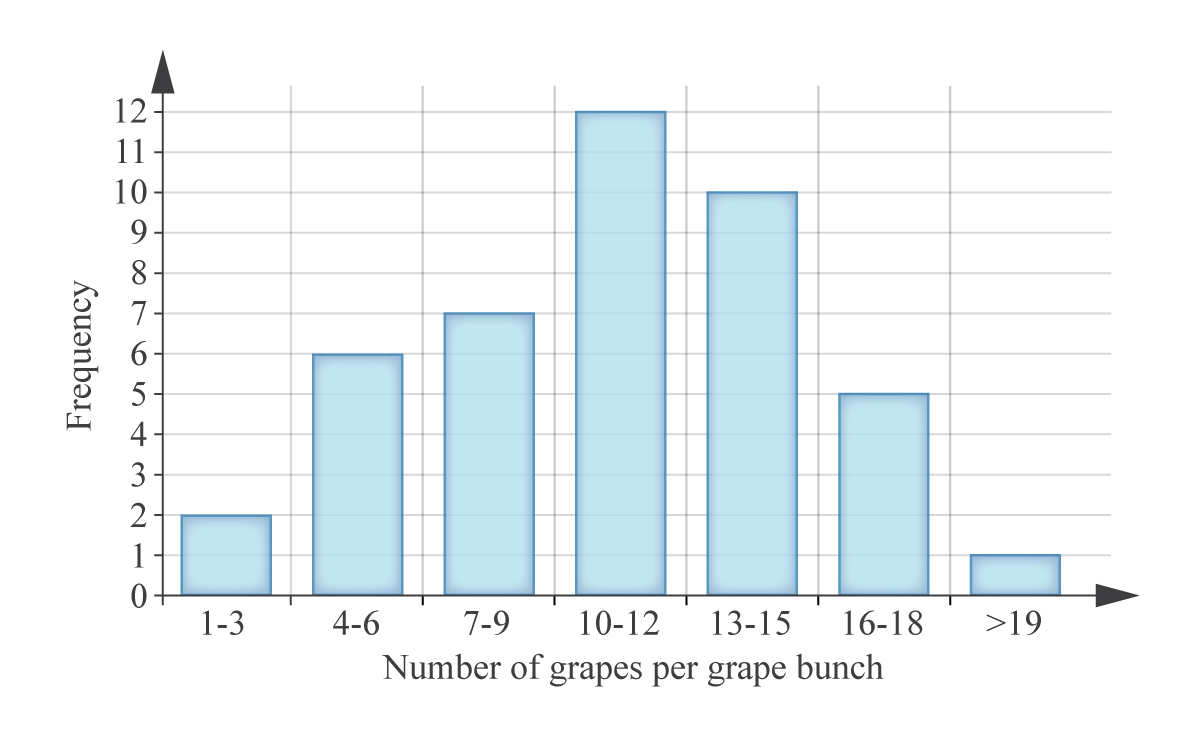 (Source: Kognity)
(Source: Kognity)
Note
If data is discrete, a gap must be left between the bars. If data is continuous, there must not be a gap between the bars.
A cumulative frequency table can be used to find the number of data values below a certain class boundary. It involves the addition of a cumulative frequency column which represents the sum of the frequency of the current class as well as every class before it. It is similar to a prefix sum array in computer science.
Example
| Height (cm) | Frequency | Cumulative frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2 | |
| 5 | 7 |
A cumulative frequency curve consists of an independent variable on the x-axis, and the cumulative frequency on the y-axis. In grouped data, the values on the x-axis correspond to the upper bound of a given class. This graph is useful for interpolation (e.g., the value of a given percentile).
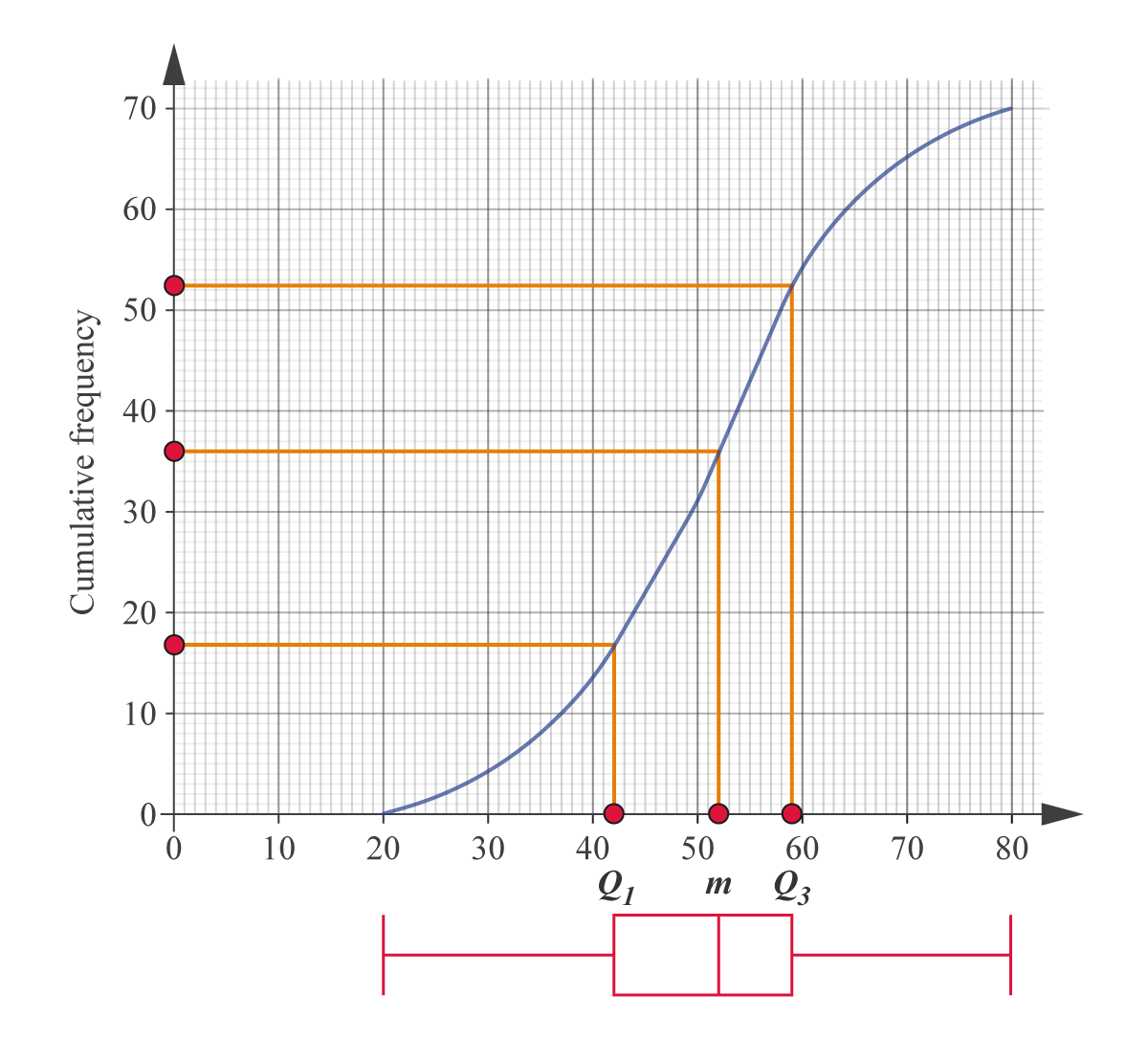 (Source: Kognity)
(Source: Kognity)
A box-and-whisker plot is a visual representation of the "5-number summary" of a data set. These five numbers are the minimum and maximum values, the median, and the first and third quartiles.
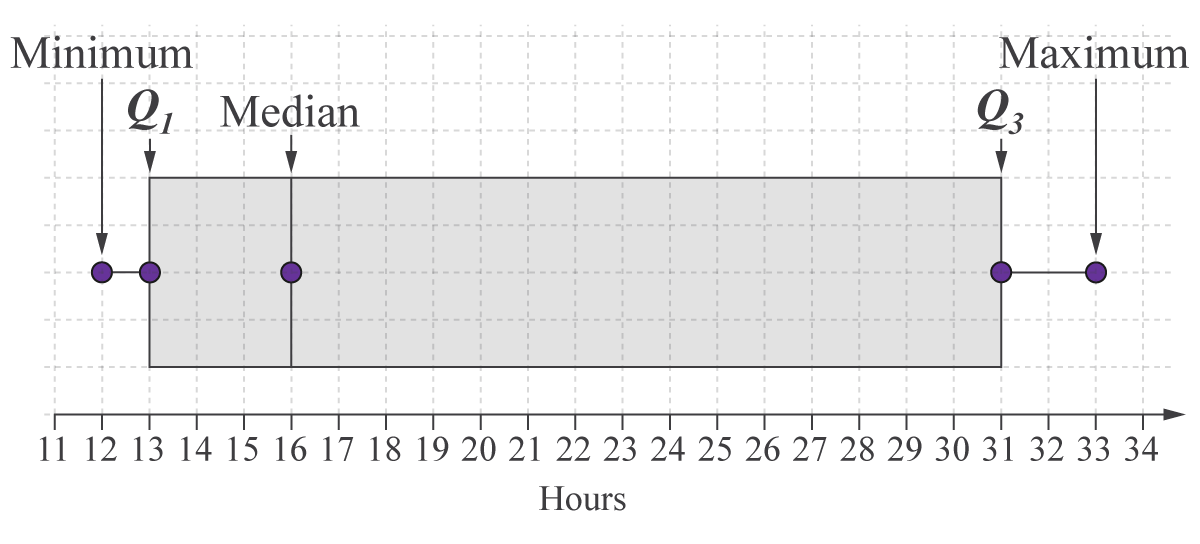 (Source: Kognity)
(Source: Kognity)
Warning
In the image above, the maximum and minimum dots are filled. If these values were to be excluded (e.g., the upper class boundary in grouped data is excluded), they should be unfilled instead.
Measures of central tendency¶
The mean is the sum of all values divided by the total number of values. represents the mean of a sample while represents the mean of a population.
where is equal to the number of values in the data set.
In grouped data, the mean can only be estimated, and is equal to the average of the sum of midpoint of all classes multiplied by their class frequency.
where is the midpoint of the th class and is the frequency of the th class.
The median is the middle value when the data set is sorted. If the data set has an even number of values, the median is the mean of the two centre-most values.
In grouped data, the median class is the class of the th value if the number of values in the class is odd or the th value otherwise.
The mode is the value that appears most often.
Definition
- Unimodal: A data set with one mode.
- Bimodal: A data set with two modes.
- Multimodal: A data set with more than two modes.
- No mode: A data set with no values occurring more than once.
In grouped data, the modal class is the class with the greatest frequency.
Measures of dispersion¶
These are used to quantify the variability or spread of the data set.
The range of a data set is simple to calculate but is easily thrown off by outliers.
The variance () and standard deviation () of a data set are more useful. The standard deviation indicates how closely the values of a data set are clustered around the mean.
where is the frequency of the th class, is the midpoint of the th class, is the mean of the whole data set, and is the number of values in the data set.
For ungrouped data, assume .
In a typical bell-shaped distribution:
- 68% of data lie within 1 standard deviation of the mean ()
- 95% of data lie within 2 standard deviations of the mean ()
- 99.7% of data lie within 3 standard deviations of the mean ()
- any data outside 3 standard deviations of the mean can be considered outliers
Info
The points of inflection (when the curve changes direction) of a normal bell curve occur at .
Data transformation¶
When performing an operation with a constant value to a whole data set:
| Operation | Effect on mean | Effect on standard deviation |
|---|---|---|
| Addition/subtraction | Increased/decreased by constant | No change |
| Multiplication/division | Multiplied/divided by constant | Multiplied/divided by constant |
Linear correlation and regression¶
Definition
- Interpolation: The prediction of values within the range of a data set.
- Extrapolation: The prediction of values outside the range of a data set. This tends to be less reliable than interpolation as it is unknown if the model is accurate outside of the range of the data set..
A scatter plot is used to help find trends and relationships between variables, which is primarily used to predict results not in the data set.
If there is a clear trend in the data, there is said to be a correlation between the independent and dependent variables.
- If the line has an upward trend, it has a positive correlation.
- If the line has a downward trend, it has a negative correlation.
The strength of the correlation ranges from none, weak, moderate, strong, and perfect, where the latter shows a line passing through all data points.
The line of best fit may not be linear. It may be quadratic, exponential, logarithmic, or there might not be a line of best fit at all. In the latter case, there is no correlation.
Correlation does not imply causation. There may be an external confounding factor which causes both trends, instead.
Example
If ice cream consumption increases as deaths from drowning increase, it does not mean that drowning causes people to eat more ice cream. The confounding factor of summer increases ice cream consumption and frequency of swimming, which leads to more people drowning.
To find the regression line (line of best fit), a mean data point is required. The mean data point is a new point located at the mean of all x- and y-coordinates, or . The regression line then is the line that passes through the mean point while minimising the vertical distance from every data point. This is most easily performed on a graphing display calculator (GDC), but can be calculated manually if needed.
The least squares regression is used to find the equation of a line that passes through the mean point for which the square of the vertical distance between the line and all data points (the residuals) is minimised for each point. It involves forming a line such that the sum of all residuals is , and the sum of all residuals squared is minimised.
Alternatively, to manually guesstimate a linear line of best fit, a line can be drawn from the mean point to a point that best appears to lie on the line of best fit.
The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (more commonly known as Pearson's or the -value) quantifies the correlation strength of a line of best fit, or how well the line of best fit fits. This value is such that , where
- is a positive correlation
- is a negative correlation
- is a perfect correlation
- is a strong correlation
- is a weak to moderate correlation
- is no correlation, so that no line of best fit can be drawn.
5 - Calculus¶
Rate of change¶
The average rate of change (ARoC) between points and is represented by the slope of the secant line (). Therefore, as slope is the difference in rise over the difference of run (), the slope of the secant line can be expressed as
This is known as the difference quotient.
The instantaneous rate of change (IRoC) at point is represented by the slope of the tangent line (). The slope of the tangent line can be found by finding the difference quotient with as a very small value, e.g., .
Warning
The above method of finding the IRoC should be disregarded in favour of finding the derivative.
Sequences¶
A sequence is a function with a domain of all positive integers in sequence, but uses subscript notation () instead of function notation ().
Reminder
- The recursive formula for a sequence is where .
- The arithmetic formula for a sequence is .
If the sequence is infinite, as becomes very large:
- If the sequence continuously grows, it tends to infinity. (E.g., )
- If the sequence gets closer to a real number and converges on it, it converges to a real limit, or is convergent. (E.g., )
- If the sequence never approaches a number, it does not tend to a limit, or is divergent. (E.g., )
Limits¶
A limit to a function is the behaviour of that function as a variable approaches, but does not equal, another variable.
Example
"The limit of as approaches is ."
If the lines on both sides of a limit do not converge at the same point, that limit does not exist.
If the lines on both sides of a limit become arbitrarily large as approaches , it approaches infinity.
One-sided limits¶
A positive or negative sign is used at the top-right corner of the value approached to denote if that limit applies only to the negative or positive side, respectively. A limit without this sign applies to both sides.
Example
- shows that as approaches from the negative (usually left) side, approaches .
- shows that as approaches from the positive (usually right) side, approaches .
- shows that as approaches from either side, approaches .
If , does not exist.
Properties of limits¶
The following properties assume that and have limits at , and that , , and are all real numbers.
Evaluating limits¶
When solving for limits, there are five central strategies used, typically in this order if possible:
Direct substitution¶
Substitute as and solve.
Example
If only direct substitution fails and returns , continue on with the following steps. If only the denominator is , the limit does not exist.
Factorisation, expansion, and simplification¶
Attempt to factor out the variable as much as possible so that the result is not , and then perform direct substitution.
Example
Rationalisation¶
If there is a square root, multiplying both sides of a fraction by the conjugate may allow direct substitution or factorisation.
Example
One-sided limits¶
There may only be one-sided limits. In this case, breaking the limit up into its two one-sided limits can confirm if the two-sided limit does not exist when looked at together.
Change in variable¶
Substituting a variable in for the variable to be solved and then solving in terms of that variable may remove a problem variable.
Example
Note
If exists and direct substitution is not possible, must be a factor of both and so that the discontinuity can be removed. Therefore, and .
Limits and continuity¶
If a function has holes or gaps or jumps (i.e., if it cannot be drawn with a writing utensil held down all the time), it is discontinuous. Otherwise, it is a continuous function. A function discontinuous at is "discontinuous at ", where is the "point of discontinuity".
A removable discontinuity occurs when there is a hole in a function. It can be expressed as when either
A jump discontinuity occurs when both one-sided limits have different values. It is common in piecewise functions. It can be expressed as when
An infinite discontinuity occurs when both one-sided limits are infinite. It is common when functions have vertical asymptotes. It can be expressed as when
Therefore, a function is only continuous at if all of the following are true:
- exists
Limits approaching infinity¶
As approaches infinity, has only three possible answers.
By dividing both sides of a fraction by the variable of the highest degree, if is the degree of the denominator and is the degree of the numerator:
- If ,
- If ,
- The sign of infinity can be found by evaluating the limit
- If , , where and are the coefficients of the degree of the numerator and the denominator, respectively.
Derivatives¶
A derivative function is a function of all tangent slopes in the original function. It can either be expressed in function notation as ("f prime of x") or in Leibniz notation as . The process of finding a derivative of a function is known as differentiation.
Note
Although evaluating a derivative function in function notation is the usual to solve for when , Leibniz notation is stupid and requires the following (the vertical bar shown should be solid):
If exists, the function is "differentiable at " such that . Functions are only differentiable at if the function is continuous at and the tangent at is not vertical.
Example
Some examples of issues that can cause are vertical asymptotes and other discontinuities, vertical tangents, cusps, and corners. The last two cause .
Finding derivatives using first principles¶
The first principles method of finding derivatives involves using simple algebra and limits. Taking the difference quotient and adding a limit of :
results in the equation of the derivative function. Direct substitution of will result in an indeterminate form, so the equation should be manipulated to remove from the denominator typically via factoring.
Example
Differentiating using first principles:
Drawing derivative functions¶
If the slope of a tangent is:
- positive/negative, that value on the derivative graph is also positive/negative, respectively
- zero, that value on the derivative graph is on the x-axis
Points of inflection on the original function become maximum/minimum points on the derivative graph.
The derivative of a linear equation is always constant, and the derivative of a constant value is ..
Derivative rules¶
These rules can be used in place of/to supplement finding derivative functions using first principles and are usually much faster to calculate. These rules assume that all of the functions involved are differentiable.
The degree of a derivative is always the degree of the original function.
The power rule applies to all functions of the form , such that:
Example
The constant multiple rule applies to all functions of the form , where is any real number, such that:
Example
The sum rule applies to all functions of the form such that:
Example
The product rule applies to all functions of the form such that:
Example
The extended product rule applies to all functions of the form such that:
The quotient rule applies to all functions of the form such that:
Example
The chain rule applies to all functions of the form such that:
Example
Trigonometric derivative rules¶
These primary derived rules can be used to further derive the derivatives of the other trignometric ratios:
The chain rule applies to trigonometric functions and will be applied recursively if needed.
Example
Trigonometric identities are not polynomial so values on an interval need to be determined by substituting values between vertical asymptotes and critical points.
Extended derivative rules¶
For an exponential function where or , respectively:
For a logarithmic function where or , respectively:
From the above base derivatives the derivatives for functions involving and the natural logarithm can be found:
This opens up the possibility of logarithmic differentiation, which is required for exponential or logarithmic functions with a variable base. The natural logarithm of both sides should be taken prior to differentiation and logarithmic rules applied to simplify the equation.
Higher order derivatives¶
The second derivative of is the derivative of the first derivative of , that is, .
The th derivative of is , and is the derivative of the th derivative. It is written as in Leibniz notation.
Example
The second derivative of an object's position with respect to time is its acceleration. See SL Physics A#Displaying motion for more information.
Interval charts¶
To identify the positive or negative regions of an equation, an interval line or chart can be used. To do so:
- Factor the equation as much as possible and identify the x-intercepts.
- Place the x-intercepts on a line.
- Find the sign of the end behaviour by taking the sign of the leading coefficient.
- When crossing an x-intercept, if the degree of that factor is even, the sign stays the same; otherwise, it alternates.
- Repeat for every other region.
Implicit differentiation¶
Implicit differentiation differentiates both sides of an equation with respect to and solves for (). Note that if is isolated, this is effectively the same as explicit differentiation. When differentiating implicitly, it must be shown that the derivative of both sides with respect to x () is being taken.
Warning
The chain rule must be applied when differentiating terms that contain .
Example
Related rates¶
When solving for questions that ask for rate of change related to other rates of change, ensure that:
- variables are defined
- equations are written in terms of derivates
- the equations are differentiated with respect to time
- apply derivative rules (especially the chain rule) to every variable that is not a constant (i.e., that changes with respect to time)
- substitute values only at the end
5.2 - Increasing and decreasing functions¶
- If in the interval , is increasing on .
- If in the interval , is decreasing on .
- If in the interval , is constant on .
- The points where are the critical/maximum/minimum points.
Functions only change whether they are increasing/decreasing/constant at the critical points/"relative extrema".
These points and whether the intervals between them increase/decrease can be found by using an interval chart/line using the first derivative.
Example
If :
- is decreasing on .
- is increasing on .
Extrema¶
Extrema are the maximum and minimum points in a function or an interval of a function. They must be at critical points—where or , and may include the boundary points if looking for extrema in a given interval.
The highest and lowest point(s) of are known as the absolute maximum/minimum of .
Any other relative/local maxima or minima are such that all of the points around that point are higher or lower.
Fermat's theorem states that if is a local extremum, must be a critical number of . Therefore, if is continuous in the closed interval , the absolute extrema of must occur at , , or a critical number.
To find the extrema of a continuous function , where is a critical value, the first derivative test may be used with the assistance of an interval chart/line. If only an interval of a function is under consideration, the boundary points must be taken under consideration as well.
- If changes from positive to negative, there is a relative/local minimum at .
- If changes from negative to positive, there is a relative/local maximum at .
- If the sign is the same on both sides, there is no extrema at .
- The greatest/least relative/local maximum/minimum is the absolute maximum/minimum.
Alternatively, the second derivative test may be used instead. At the critical point where , a positive indicates a local minimum while a negative indicates a local maximum. If , the test is inconclusive and the first derivative test must be used.
Example
The absolute minimum of is at . There is no absolute maximum nor are there any other relative/local maximum/minimum points.
Warning
- There can be multiple absolute maxima/minima if there are multiple points that are both highest/lowest.
- If a function is a horizontal line, the absolute maximum and minimum for is .
Concavity¶
Definition
A point of inflection on a curve is such that and the signs of around the point change (e.g., positive to negative).
- An interval is concave up if it increases from left to right and tangent lines are drawn below the curve, so . It is shaped like a smile.
- An interval is concave down if it increases from left to right and tangent lines are drawn above the curve, and . It is shaped like a frown.
Changes in concavity only occur at points of inflection.
Cusps¶
A cusp is a point on a continuous function that is not differentiable as the slopes on both sides approach -∞ and ∞. Concavity does not change at a cusp, but they may be considered for local extrema.
Optimisation¶
To optimise for a maximum or minimum of a variable:
- Identify an equation with only one variable dependent on another
- Find the first derivative and identify critical points
- Use the second derivative test to identify if the critical point is a maximum or minimum
- Check constraints and throw away any inadmissible results
Diagrams with labelled variables may be helpful.
Asymptote behaviour¶
The vertical asymptotes of a function are at values of that make the denominator of the simplified function . The behaviour near them can be found using limits as approaches those points.
The horizontal asymptotes of a function can be found as approaches positive and negative infinity. To determine behaviour near them, the sign of , where is the y-coordinate of the asymptote. A positive limit indicates that is above the asymptote while a negative limit indicates that is below the asymptote.
Curve sketching¶
- Determine the domain of the function and consider discontinuities (holes and asymptotes)
- Determine the y-intercept and if easy, x-intercepts
- Determine the behaviour near vertical and horizontal asymptotes
- Identify critical points by solving or
- Use the first or second derivative tests to test critical points
- Identify points of inflection by solving or and test concavity on both sides of possible points
Resources¶
- IB Math Analysis and Approaches Syllabus
- IB Math Analysis and Approaches Formula Booklet
- Calculus and Vectors 12 Textbook
- Course Pack Unit 1: Descriptive Statistics (Annotated)
- Course Pack Unit 2: Limits and Rate of Change (Annotated)
- Course Pack Unit 3: Derivatives and Applications (Annotated)
- Course Pack Unit 4: Curve Sketching and Optimisation (Annotated)
- Course Pack Unit 5: Trigonometric, Exponential, and Logarithmic Functions (Annotated)
- TI-84 Plus Guide